|
||
|
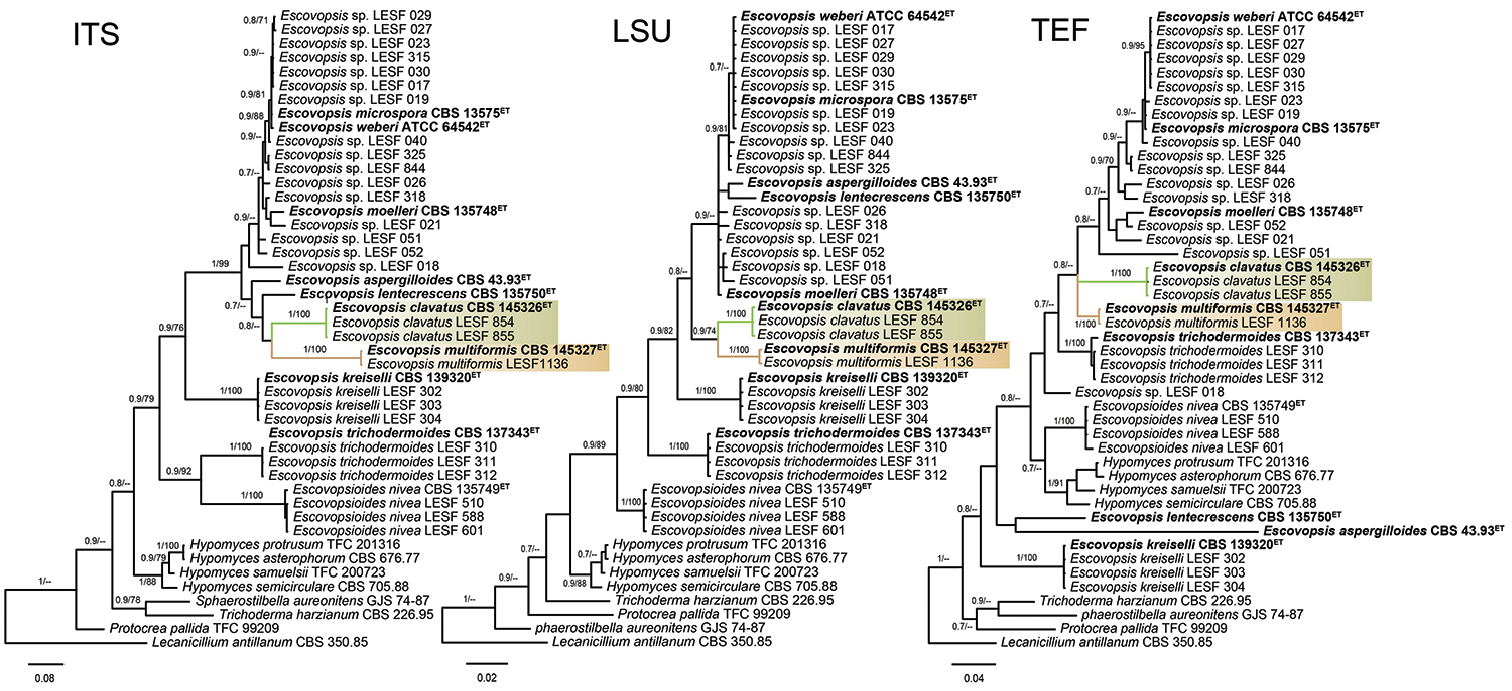
Phylogenetic position of Escovopsis clavatus and Escovopsis multiformis considering each molecular marker separately (ITS, LSU and tef1). The trees were reconstructed under Bayesian and Maximum Likelihood inferences. The numbers on branches indicate the posterior probabilities and the bootstrap support values, respectively. The seven Escovopsis ex-type strains are denoted in bold and the new species are highlighted in green (E. clavatus) and light brown (E. multiformis). The trees include a total of 46 Escovopsis sequences of each marker (ITS – 619 bp, LSU – 594 bp and tef1 – 758 bp) and Escovopsioides, Hypomyces, Sphaerostilbella, Trichoderma and Protocrea were included as the closest phylogenetic relatives of Escovopsis. Lecanicillium antillanum CBS 350.85 was used as the outgroup. ET: ex-type. |