|
||
|
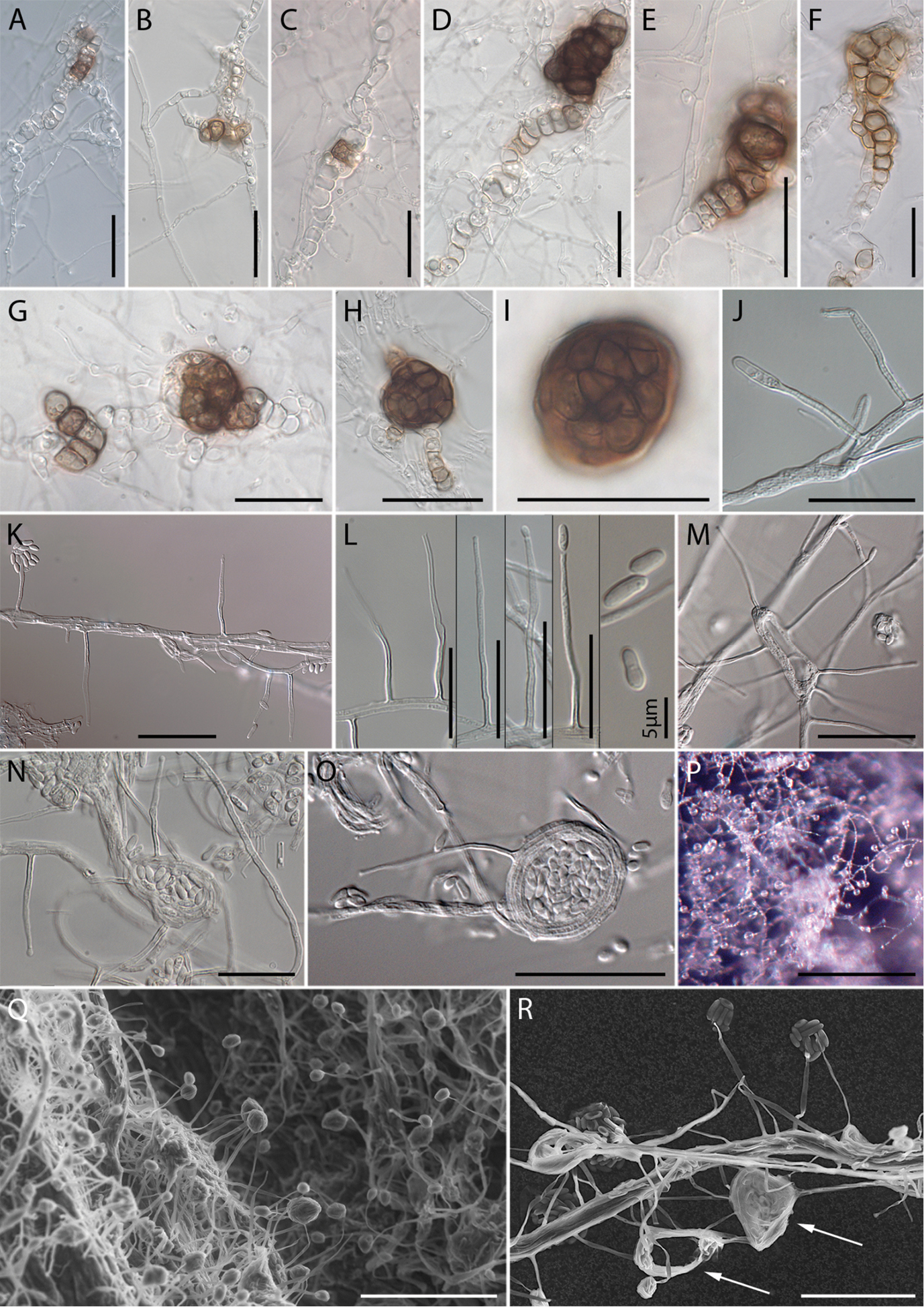
Micrographs of Monocillium gamsii. A–C Hyphal growth by intercalary development of chlamydospore and dityochlamydospore-like structures filled with guttules D–H initiation of microsclerotia by interweaving or coiling of dictyochlamydospores, and growth to full size I Highly pigmented sclerotium at maturity displaying a textura angularis on surface view J–N Setae, phialides and conidia M–O Formation of phialides on coiling hyphae P Conidial heads, conidia cohering in wet heads Q, R SEM: Q Phialides from mycelium with conidial heads, arising from hyphae R coiling hyphae (arrows), and detail of phialides bearing conidia A–I from PDA 1/3 strength J–P from PDA; Q, R from OA. Scale bars: 30 µm (A, H, I, K, M, O, R); 20 µm (B–G, J, L, N); 200 µm (P), 50 µm (Q). |