|
||
|
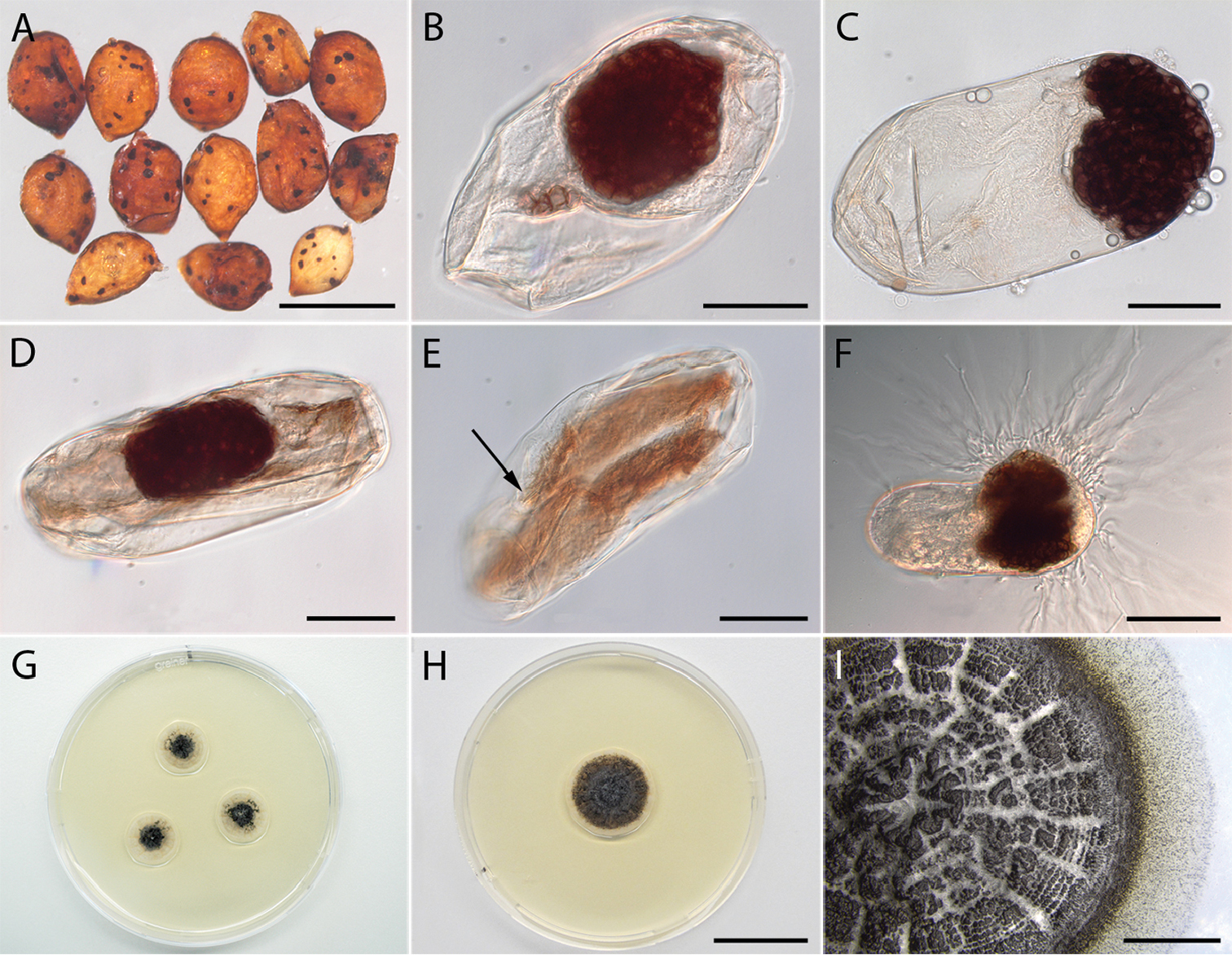
Naturally infested cysts and eggs of Heterodera filipjevi with Monocillium gamsii, and pure cultures obtained from infected eggs. A Field collected symptomatic cysts bearing parasitised eggs. B–E Nematode eggs infected by M. gamsii B, D Nematode eggs containing microsclerotia of M. gamsii E An embryonated egg containing a second stage juvenile (J2) parasitised by M. gamsii (arrow points at nematode’s stylet) F A nematode egg containing microsclerotia, and hyphae growing out of it G–H colony of M. gamsii grown on PDAG colonies developing from three individually plated infected eggs H A 25-d-old culture grown at 25 °C in the dark I The surface of a five-month-old culture detailing the sclerotioid masses covering the colony surface. Single microsclerotia can be seen as little black dots at the margin of the culture. Scale bars: 800 µm (A); 30 µm (B–E); 50 µm (F); 2 cm (H); 5 mm (I). |