|
||
|
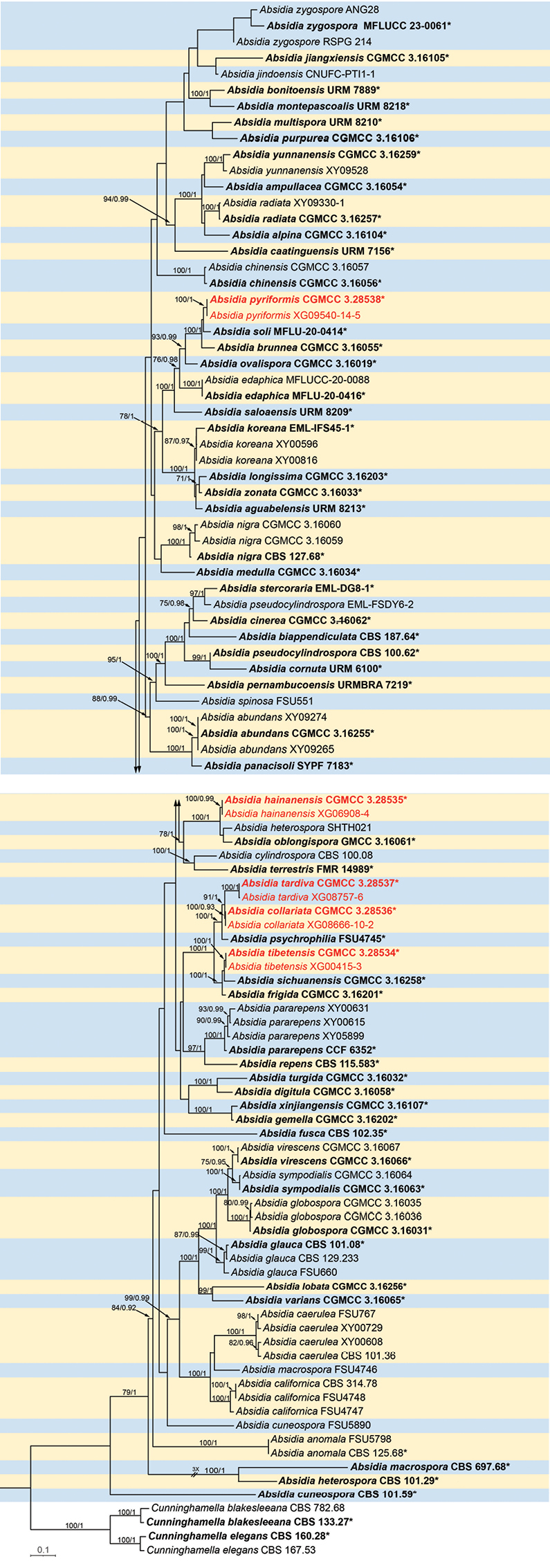
Phylogram of the genus Absidia based on a concatenated ITS, LSU, TEF1α, Act, and SSU sequence alignment, with Cunninghamella elegans and C. blakesleeana serving as outgroups. The robustness of branches is marked at the node with the Maximum Likelihood Bootstrap Value (left, MLBV ≥ 70%) and Bayesian Inference Posterior Probability (right, BIPP ≥ 0.90), which are separated by a slash “/”. Ten newly isolated strains are indicated in red bold. Branches shortened to fit the page are indicated by a double slash “//”. Bold strains marked with a star marker “*” are ex-types or ex-holotypes. The scale at the bottom left indicates 0.1 substitutions per site. |